Cytokines and growth factors
Cytokines and growth factors signal through specific receptors, controlling the metabolism and function of all cell types in the body. They, along with products that modulate their activity, are used in treating a wide variety of pathological conditions. Their value as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of diseases is increasing, along with their use in the production of other biological medicines.
What we do
Our group aims to:
Standardisation
WHO International Standards and Reference Reagents
The inclusion of WHO reference standards (where available) in bioassays is a regulatory requirement.
The use of a single primary WHO standard to calibrate secondary/local standards, harmonises and reduces variability in results, across multiple laboratories. In some cases, the standards can also be used for other purposes such as calibration of immunoassays, including commercially available kits as per recommendations. For example, the infliximab and adalimumab international standard (IS) for bioactivity determination have also been recommended for use in therapeutic drug monitoring to facilitate a harmonised approach to clinical decision making.
We have established a diverse portfolio of over 80 reference standards comprising fusion proteins, derivatised proteins and biotherapeutic monoclonal antibodies. However, the need for bioactivity standards continues to increase due to:
- the high number of novel therapeutics in development
- the identification of cytokines as novel targets
- intense activity in biosimilar medicines including monoclonal antibodies
- their use as raw materials for advanced therapy products (as stated in the Ph.Eur)
Examples of standards in the pipeline are provided below:
Pipeline of monoclonal antibody (mAb) standards
Name | Target/Critical reagent | Anticipated mAb standard |
Status |
|---|
| Bevacizumab |
VEGF
|
2019/2020 |
New IS |
| Ustekinumab |
P40 subunit of IL-12/IL-23
|
2021/2022 |
New IS |
For some products, such as Bevacizumab, it is also important to standardise the target protein, VEGF, which serves as the critical reagent in bioassays. Some critical reagents for monoclonal antibodies are available as WHO reference standards from NIBSC and a program to deliver working standards for these has also been initiated.
To donate materials for reference standards or critical reagents (e.g. VEGF, IL-6, IL-23) or to participate in collaborative studies, contact enquiries@nibsc.org.
Reference standards and methods for immunogenicity evaluation
Treatment with a biotherapeutic often elicits formation of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) that can impact on clinical efficacy and patient treatment. ADA monitoring of patients for clinical decision-making is gaining momentum, however measuring ADAs is challenging and efforts to standardise such assays are recognised as an important step towards ensuring comparability of results. Our activities include:
Efforts to develop antibody standards/panels for monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapeutics such as infliximab, adalimumab, rituximab are being planned.
To participate in collaborative studies, contact enquiries@nibsc.org.
Control
We assess the quality of products such as biosimilar medicines to support public health, by responding to incidents such as the TGN 1412 clinical trial and testing falsified medicines/counterfeits seized by MHRA’s enforcement group.
Find out more about NIBSC control testing.
Research
Bioassay Development
Our expertise lies in developing novel or refining existing in vitro analytical assays and we have contributed to the development of assays for several cytokines and understanding adverse effects of biological medicines such as TGN1412.
Find out more from research published in British Journal of Pharmacology.
Recent work has focused on developing assays for mAb bioactivity. This includes antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) assays using surrogate effector cells as opposed to traditional primary cell based assays. We characterised an assay using the B cell-line, Raji (target) and the surrogate CD16 expressing luciferase reporter cell-line, J9 (effector) containing an additional constitutively expressed reporter gene that allows for fluctuations in cell number and viability. We have applied this method to testing of rituximab products and the international collaborative study for this standard.
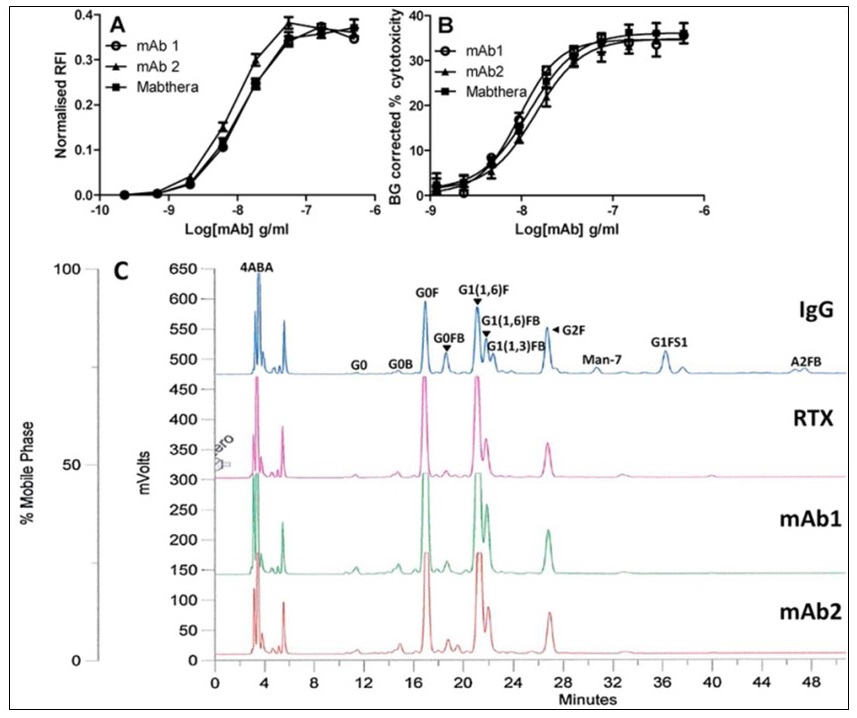
Mabthera (the innovator product) compared with two rituximab biosimilars (mAb 1, 2) in development using A: Surrogate ADCC assay and B: CDC assay. C: Data from N-glycan analysis of PNGase F released N-glycans including IgG from human serum as a standard for N-glycan species.
Immunogenicity
Testing for unwanted immunogenicity is a regulatory requirement for approval of biotherapeutic products. This includes validated anti-drug antibody (ADA) assays, since the impact of ADA on clinical outcome is critical. Our activities include:
Fundamental biology
Since dysregulation of cytokines can result in disease pathology and progression, an understanding of the fundamental biology of these molecules is important in elucidating their role in disease settings.
Our projects
Exploring the biology of IL-27 in human leukemic cells
We investigated the effect of IL-27 on the growth and survival of various human leukemic cell lines and on chemotherapy and showed new properties of IL-27 in tumour promotion and the inhibition of chemotherapeutic response. This suggests IL-27 as a potential therapeutic target for certain subtypes of human leukaemia. Find out more about this research in Journal of Interferon and Cytokine Research.
Thrombotic microangiopathy and Interferon (IFN) therapy
IFN-α and IFN-β have been linked to thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), a rare and life-threatening disorder affecting renal functions. To understand the molecular basis for the TMA in IFN treated patients, we investigated the in vitro effects of IFN on endothelial cell functions associated with angiogenesis and blood haemostasis. Results suggest that IFN interferes with angiogenesis and fibrinolysis through downregulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and upregulation of the potent inhibitor PAI-1 produced by vascular endothelial cells – this could potentially cause the loss of physiological endothelium thromboresistance and facilitate development of vascular complications in a clinical setting. This study was published in Thrombosis Research.
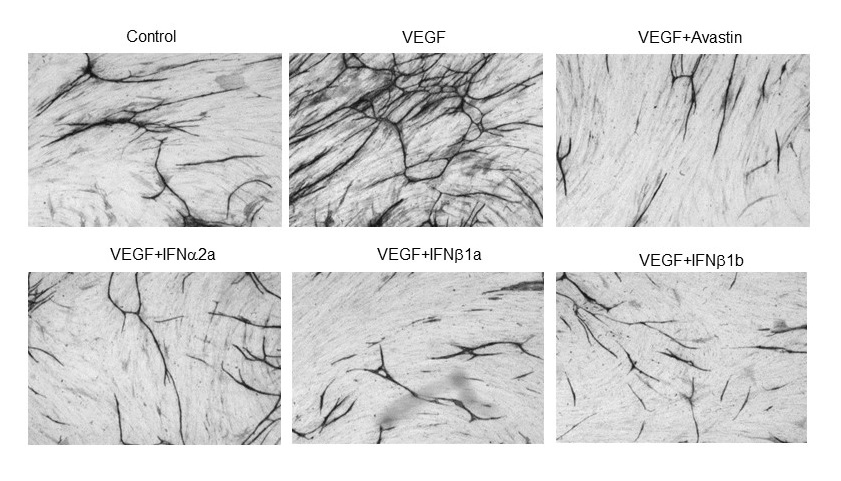
A co-culture model of angiogenesis, both IFN-α and IFN-β strongly inhibited VEGF-induced development of capillary-like structures in a manner comparable to avastin (bevacizumab, anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody).
Redox regulation of biotherapeutics
In inflammatory diseases and cancers, cells secrete thiol reductases (thioredoxin, TRX and protein disulfide isomerase, PDI) which can modify the disulfide bonding structure of extracellular proteins affecting function and signalling. Therapeutic mAbs have revolutionized the treatment of these diseases but many patients do not respond to treatment or develop ADAs which impacts on clinical efficacy. We are investigating whether TRX and PDI have a role to play in the reduced efficacy of such therapies.