Glycan Analysis
Protein glycosylation can play an important role in defining in vivo bioactivity, stability, solubility and metabolic fate of biotherapeutics. Glycosylation is a post-translational modification and, unlike transcription, is a non-template-driven enzymatic modification process – its structural status depending largely on production methods and conditions. For this reason the product can vary when it is being made.
Monitoring protein glycosylation is increasingly important since more novel recombinant glycoprotein therapeutics – such as glycoprotein hormones, cytokines, clotting factors and monoclonal antibodies – are in clinical use. Pharmacopoeias of European, US and the Far Eastern regulatory authorities are actively developing appropriate monographs to account for these new drug substances. The areas they are looking at are:
- identifying glycosylation profiles to monitor critical glycan structures that are important for activity or adverse effect
- monitoring glycan profiles for production consistency
- developing appropriate level of deviation allowed for control
- harmonisation and choice of methodologies
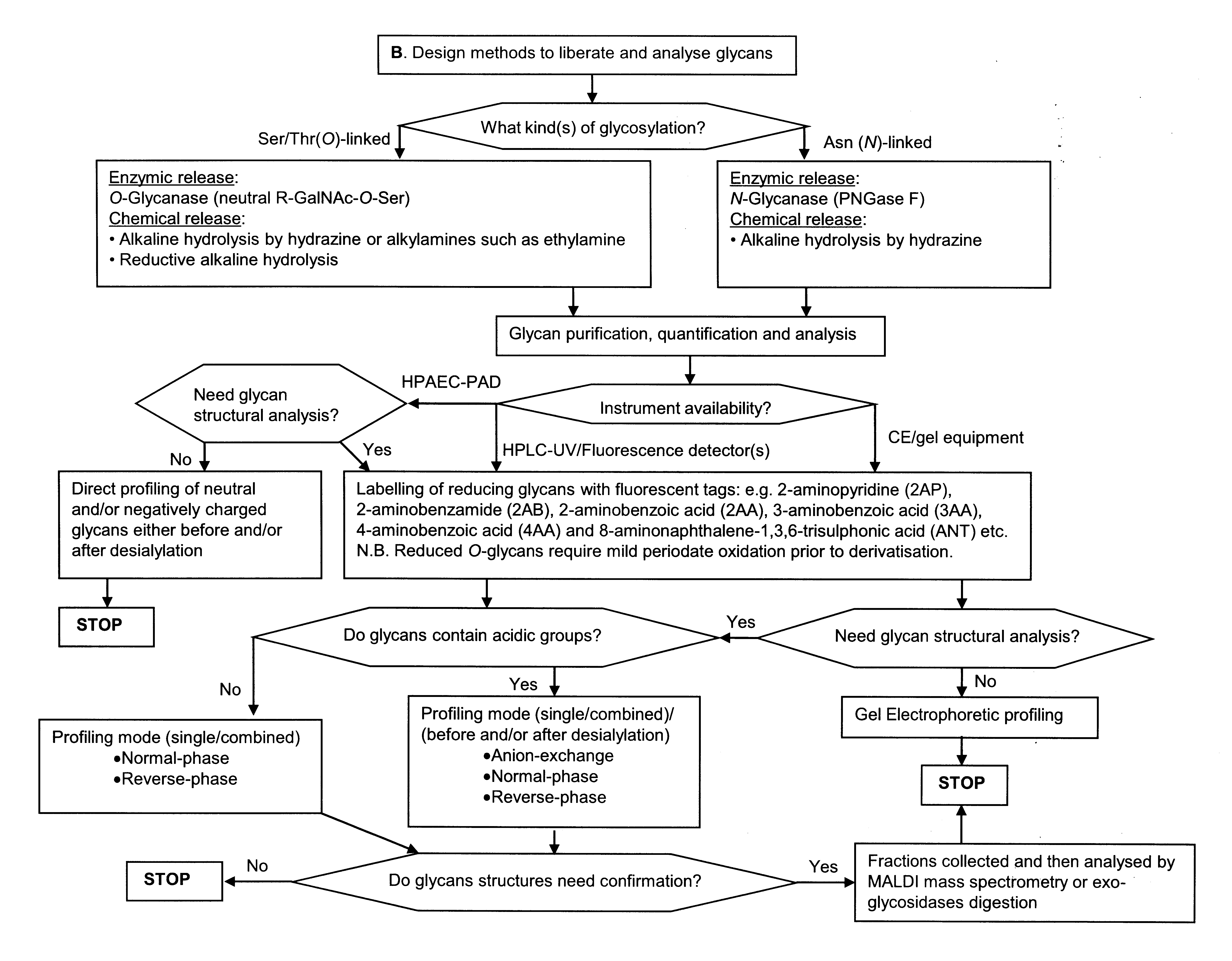
There are two main types of protein glycosylation: N-, asparagine (Asn)-linked and O-, serine/threonine (Ser/Thr)-linked. We can analyse protein glycosylation with some general established techniques:
- isoelectric focusing (IEF) polyacrylamide gel (PAGE) electrophoresis for intact glycoproteins
- capillary electrophoresis (CE) for intact glycoproteins
- mass spectrometry (MS) for glycopeptides and released glycans
- high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for labelled or un-derivatised released glycans through:
> normal phase or hydrophilic interaction HPLC (HILIC)
> reverse phase HPLC
> weak anion exchange (WAX) HPLC
> high pH anion exchange chromatography (HPAEC)
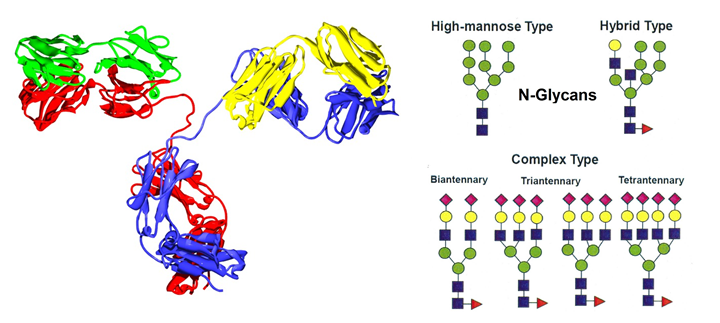
Because glycan structures are so diverse and complex, and taking into account that detection systems and technology are improving and increasingly available, there is a wide range of analysis methods. These methods have different approaches and modifications depending on availability of equipment, expertise and preference of individual scientist and group. The choice of methodology is also dictated by the quantity and homogeneity of the glycoprotein product available.
Glycan group
We have a range of day-to-day services and research that we carry out at NIBSC. These include developing, preparing and evaluating glycan reference standards and evaluating proposed pharmacopoeia monographs for glycoprotein glycans analysis.
We also have a strong advisory role for different organisations. Our group is a member of the ad hoc advisory panel for the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) on Glycoprotein and Glycan Analysis (2006 to 2015), drafting and updating relevant monographs. We perform the same role for the Expert Panel for the British Pharmacopoeia and European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and Healthcare (EDQM) European Pharmacopoeia Glycan Mapping Working Group, GLM (2007-2016).
Flow Charts A and B shows decision making in glycan analysis for a drug substance