WHO 1st International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F
The WHO 1st International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F (NIBSC panel code 16/120) is intended for use as a primary standard for calibrating secondary standards, assays and kits for JAK2 V617F detection.
The panel comprises seven freeze-dried human genomic DNA materials produced by the combining of genomic DNA derived from JAK2 wild-type and JAK2 V617F cell lines, providing standards at a range of clinically relevant JAK2 V617F levels, expressed as JAK2 V617F as a percentage of total JAK2: 100% JAK2 V617F (15/164), 89.5% (15/246), 29.6% (15/244), 10.8% (15/166), 1.00% (15/168), 0.03% (15/170) and 0% (15/172).
The materials were tested by external laboratories to show suitability as standards by giving satisfactory results in allele-specific (AS)-QPCR, digital PCR, allelic discrimination-based endpoint PCR (including AS-PCR, Amplification Refractory Mutation System-PCR (ARMS-PCR) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometric analysis) and next-generation sequencing.
The panel was established in 2016 by the Expert Committee on Biological Standardization of the World Health Organization as the 1st WHO International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F, NIBSC code 16/120. The materials are endorsed by MPN&MPNr-Euronet and European LeukemiaNet.
The panel’s performance has since also been verified with the QIAGEN ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR kit CE. At the request of the JAK2 V617F diagnostic community, a small performance evaluation of the panel with this kit was performed, to determine both the panel’s usability with the kit, and the alignment of the results to that of other commonly-used JAK2 V617F diagnostic techniques. There was no significant difference between the kit and collaborative study data (Figure 1), demonstrating both the appropriateness of the panel’s use with this kit, and the suitability of the kit in providing JAK2 V617F data which is in agreement with other commonly-used diagnostic techniques.
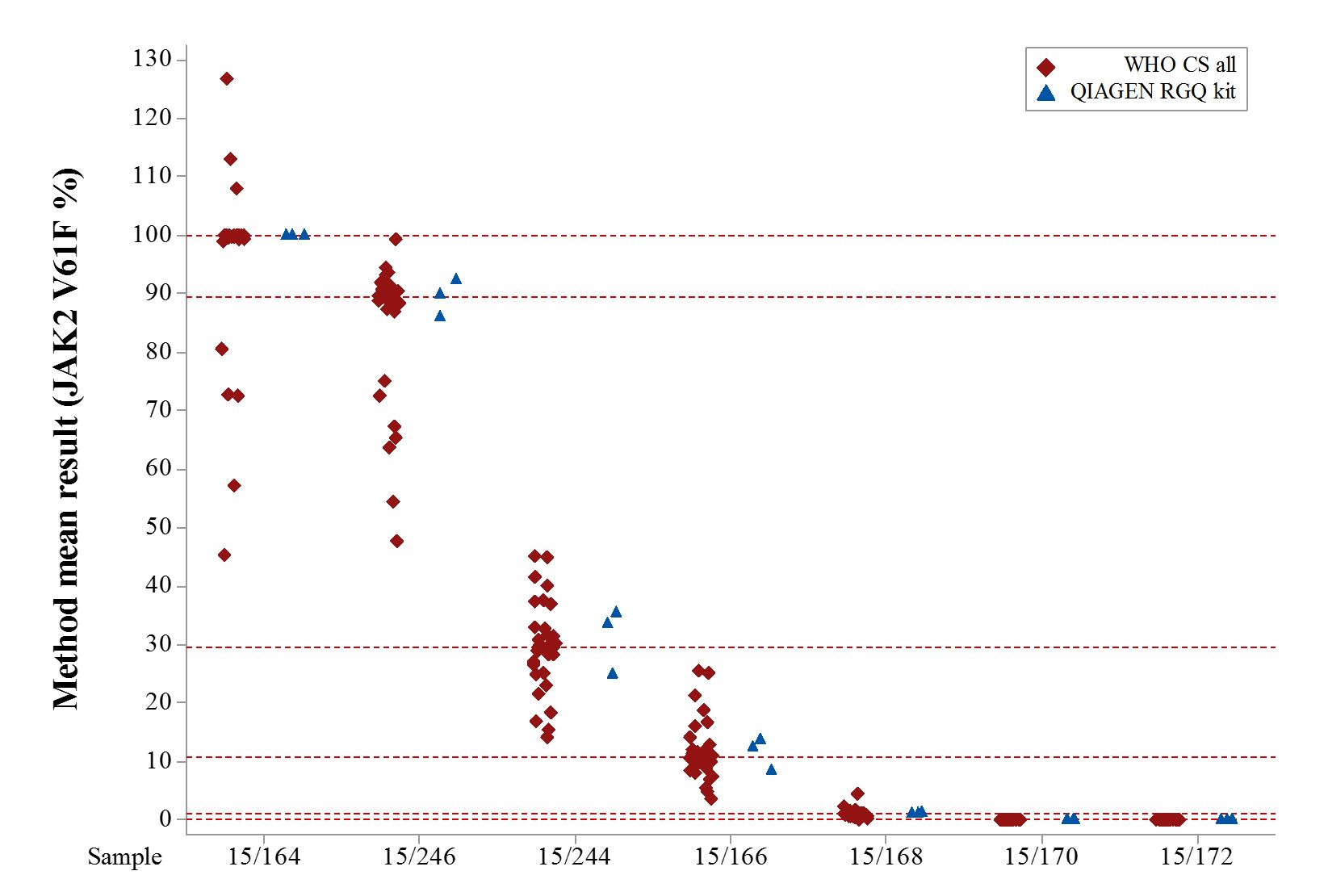
Figure 1. Mean JAK2 V617F percentage values for triplicate tested materials in all quantitative methods of the collaborative study to evaluate the proposed WHO 1st International Reference Panel for JAK2 V617F (n=32-34, each represented by a red diamond), compared with the panel’s performance evaluation with the QIAGEN ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR kit CE (n=3, each represented by a blue triangle). Red dashed horizontal lines indicate the established consensus value (% JAK2 V617F) for each of the materials, except 15/172 (consensus value 0% JAK2 V617F).
The data from this QIAGEN ipsogen JAK RGQ PCR kit CE performance evaluation are not intended to contribute to the panel members’ consensus values, but indicate the similar performance of the panel with this kit, and thus enable better standardisation across JAK2 V617F diagnostic approaches with a range of commonly-used techniques.
JAK2 V617F in Disease and Diagnostics
Chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) is a disease group comprising polycythaemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythaemia (ET), primary myelofibrosis (PMF) and chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML). The Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) mutation p. Val617Phe (c. 1849G>T; commonly abbreviated to V617F) was discovered in 2005 and determined to be present in approximately 97% of patients with PV and 50 to 60% of patients with ET and PMF. The mutation results in constitutive activation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase and increased blood cell production, and is established to be a primary molecular event causing PV.
The JAK2 V617F protein is an obvious candidate for drug-targeting, with inhibitor drugs in ongoing development; ruxolitinib was US Food and Drug Administration-approved in 2011 and European Medicines Agency-approved in 2012. It is therefore important to diagnose JAK2 V617F positive patients and monitor treatment response by the quantification of JAK2 V617F; the detection of JAK2 V617F is included in the WHO criteria for the diagnosis of MPN.
A JAK2 V617F molecular assay should be both specific for the mutation and at least sensitive enough to detect a 1% mutation burden, the clinically significant threshold for MPN diagnosis. However, with residual disease monitoring following treatments which can effectively reduce the mutation burden to zero, such as pegylated interferon-alpha-2a, the detection of JAK2 V617F at levels as low as 0.1% requires increasingly accurate and sensitive assays.
The availability of JAK2 V617F primary standards should improve the quality of MPN genomic diagnostics by enabling the calibration of assays and kits, and the derivation of secondary standards for routine diagnostic use in determining testing accuracy and sensitivity, thus providing inter-laboratory comparison towards the harmonisation of JAK2 V617F testing.
All feedback welcome to grmteam@nibsc.org.
Reference
Sanzone AP et al. (2016) Collaborative study to evaluate the proposed WHO 1st International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F
How to order
To place an order please login to your account or sign up for a new account.
For scientific enquiries contact the team at grmteam@nibsc.org.